WHY THIS MATTERS IN BRIEF
Big tech companies watch you from the outside, now they can watch you from the inside, literally. And it also has medical applications …
 Love the Exponential Future? Join our XPotential Community, future proof yourself with courses from XPotential University, connect, watch a keynote, read our codexes, or browse my blog.
Love the Exponential Future? Join our XPotential Community, future proof yourself with courses from XPotential University, connect, watch a keynote, read our codexes, or browse my blog.
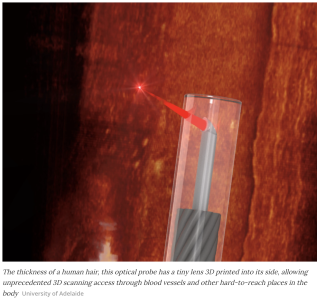
Cameras are getting smaller every day it seems, like this one that has sharper focus than an Eagle and is smaller than the width of a human hair, and they’re also getting more powerful – so powerful that new Terahertz cameras can scan the inside of your body from the outside! And who knows, maybe while it’s scanning your insides it’ll find the world’s tiniest house … Now though an Australian-German team have announced they’ve developed the world’s smallest image sensor that’s no larger than the thickness of a human hair that can scan you from the inside too. They also announced that it’s capable of traveling down the blood vessels of mice, offering unprecedented abilities to 3D scan the body at microscopic resolutions.
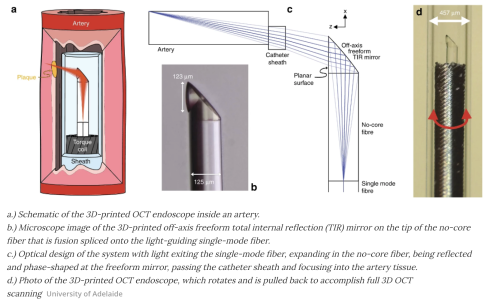
In order to build their miniature endoscope the team took a fine optical fiber with a diameter of less than half a millimeter (0.02 in), including its protective sheath. The researchers then used a 3D micro-printing technique to print a minuscule side-facing lens into it with a diameter less than 0.13 mm (0.005 in) – too small to be seen with the naked eye.
This optical fiber was then connected to an Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) scanner as a flexible probe. OCT is a 3D depth sensitive scanning technology that’s commonly used to map the retina in optometry and ophthalmology which uses near-infrared light to penetrate into tissue, measuring the wave interference between a reference beam and a probe beam to build up live 3D images that can look through surfaces within the body into the structures beneath at microscopic resolutions.
With this breakthrough, the team has built an OCT scanning device small enough to be pushed through blood vessels in the body. This ultra-thin probe can be rotated and slowly pulled backwards to build up a 3D map of its surroundings to a depth around half a millimeter below the surface. It offers unprecedented abilities to scan the vascular system of the body for the plaques, made up of fats, cholesterol and other substances, that tend to build up in blood vessel walls and lead to heart disease.
The team performed successful tests of the device in both human and mouse blood vessels, demonstrating its ability to deliver quality OCT images and the flexibility to get where it needs to go in the body. Its precisely printed lens allows the scanner to image depths five times deeper than previous attempts, and the researchers believe this tiny probe could open up new scanning options in hard-to-reach places like the cochlea of the ear and potentially even parts of the nervous system.
The team comprised medical clinicians and engineers from the University of Adelaide and the University of Stuttgart.
The study is available in the journal Light Science & Applications.
Source: University of Adelaide